Waterjet vs Plasma vs Laser – Which is Best For Your Needs?
Sommario
“Precision Cutting Solutions – Waterjet, Plasma, Laser: Tailored to Your Project’s Demands”
introduzione
When it comes to cutting through materials for manufacturing, fabrication, or artistic purposes, three of the most popular methods are waterjet, plasma, and laser cutting. Each technique offers distinct advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different applications, materials, and precision requirements. Waterjet cutting utilizes a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasive particles, to erode material away. Plasma cutting involves a superheated, electrically ionized gas to melt and cut conductive materials. Laser cutting, on the other hand, uses a focused beam of light to heat, melt, or vaporize material. The choice between waterjet, plasma, and laser cutting depends on factors such as the type of material, thickness, desired edge quality, cutting speed, and cost-efficiency. Understanding the unique properties of each method is crucial in determining which is best suited for your specific needs.
Comparing Cutting Technologies: Waterjet, Plasma, and Laser
Title: Waterjet vs Plasma vs Laser – Which is Best For Your Needs?
In the realm of industrial cutting, three technologies stand out for their precision and versatility: waterjet, plasma, and laser cutting. Each method offers unique advantages and limitations, making the choice between them a matter of matching the technology to the specific needs of the project at hand. Understanding the fundamental differences between these cutting technologies is crucial for manufacturers and fabricators who strive to optimize their production processes and ensure the highest quality in their finished products.
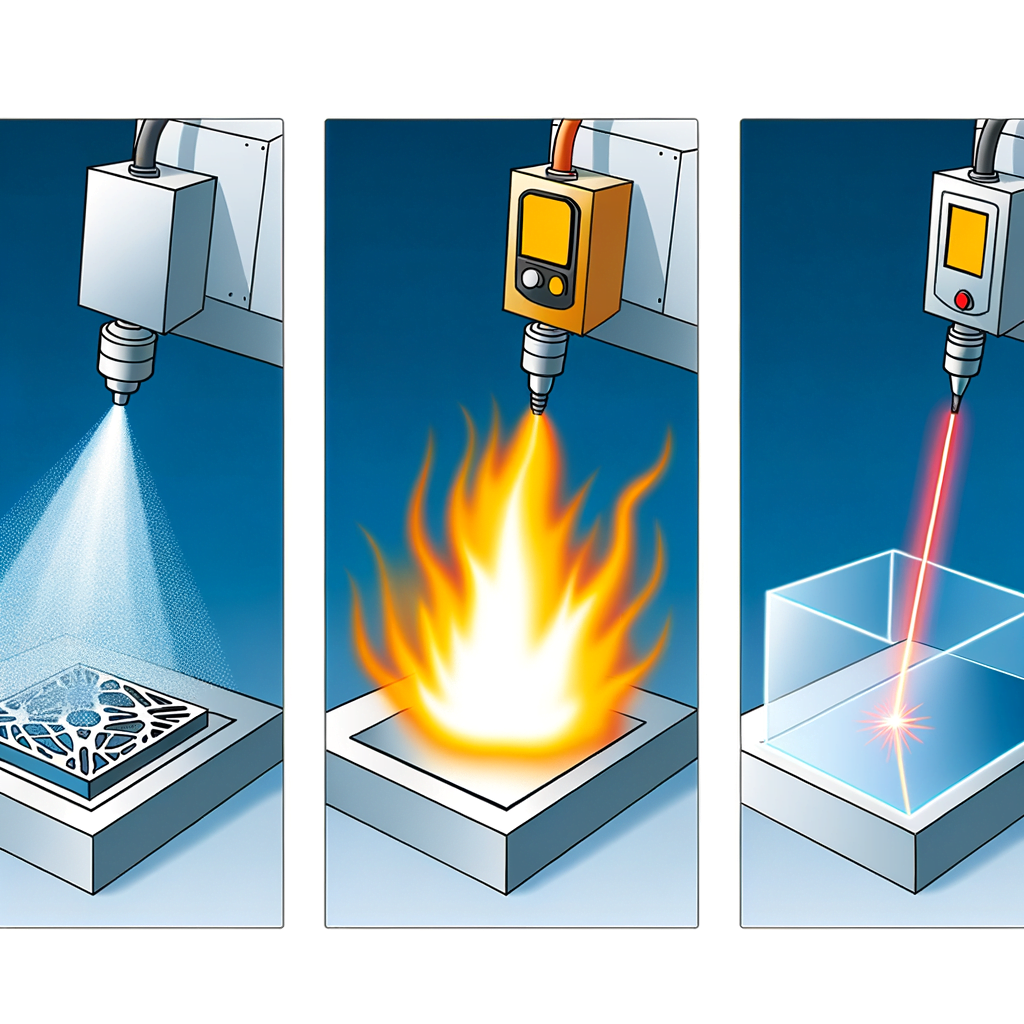
Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasive particles, to cut through materials. This method is renowned for its ability to slice through a vast array of materials, including metals, stone, and composites, without introducing heat or significant mechanical stress. Consequently, waterjet cutting is ideal for materials that are sensitive to high temperatures, as it eliminates the risk of thermal distortion or hardening at the cut edges. Moreover, waterjet cutting is highly precise and leaves a smooth finish, reducing the need for secondary processing. However, it is generally slower than plasma or laser cutting and can be more expensive due to the cost of abrasive materials and the maintenance required for the high-pressure system.
Transitioning to plasma cutting, this technique utilizes a jet of ionized gas heated to an extremely high temperature to melt and expel material from the cut. Plasma cutting is particularly effective for cutting thick metal sheets and is prized for its speed and efficiency. It is less precise than waterjet and laser cutting, which can be a drawback for applications requiring intricate detail or tight tolerances. Additionally, plasma cutting generates heat-affected zones and may lead to material warping, making it less suitable for heat-sensitive applications. Despite these limitations, plasma cutting remains a popular choice for heavy industrial use due to its cost-effectiveness and rapid cutting speeds.
Laser cutting, on the other hand, harnesses the power of a focused laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize material. This technology offers exceptional precision and is capable of producing intricate cuts with a high degree of repeatability. Laser cutting is well-suited for thin to medium-thickness materials and is commonly used for metals, plastics, and textiles. The process is clean and efficient, with a minimal heat-affected zone, which makes it a good option for materials that cannot tolerate excessive heat. However, laser cutting equipment can be costly to purchase and operate, and the cutting speed can decrease significantly as material thickness increases.
When deciding between waterjet, plasma, and laser cutting, several factors must be considered. The type and thickness of the material to be cut, the desired precision and quality of the cut edges, the acceptable level of thermal distortion, and the overall cost and speed of the cutting process are all critical considerations. Waterjet cutting is the go-to choice for diverse materials and heat-sensitive applications, while plasma cutting is favored for its speed and cost-effectiveness in cutting thick metals. Laser cutting stands out for its precision and clean cuts, especially in thin to medium-thick materials.
In conclusion, there is no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to choosing the best cutting technology. Each method has its place within the manufacturing industry, and the optimal choice depends on the specific requirements of the project. By carefully evaluating the material properties, desired outcomes, and production constraints, manufacturers can select the cutting technology that best aligns with their needs, ensuring both efficiency and quality in their finished products.
How to Choose Between Waterjet, Plasma, and Laser Cutting for Your Project
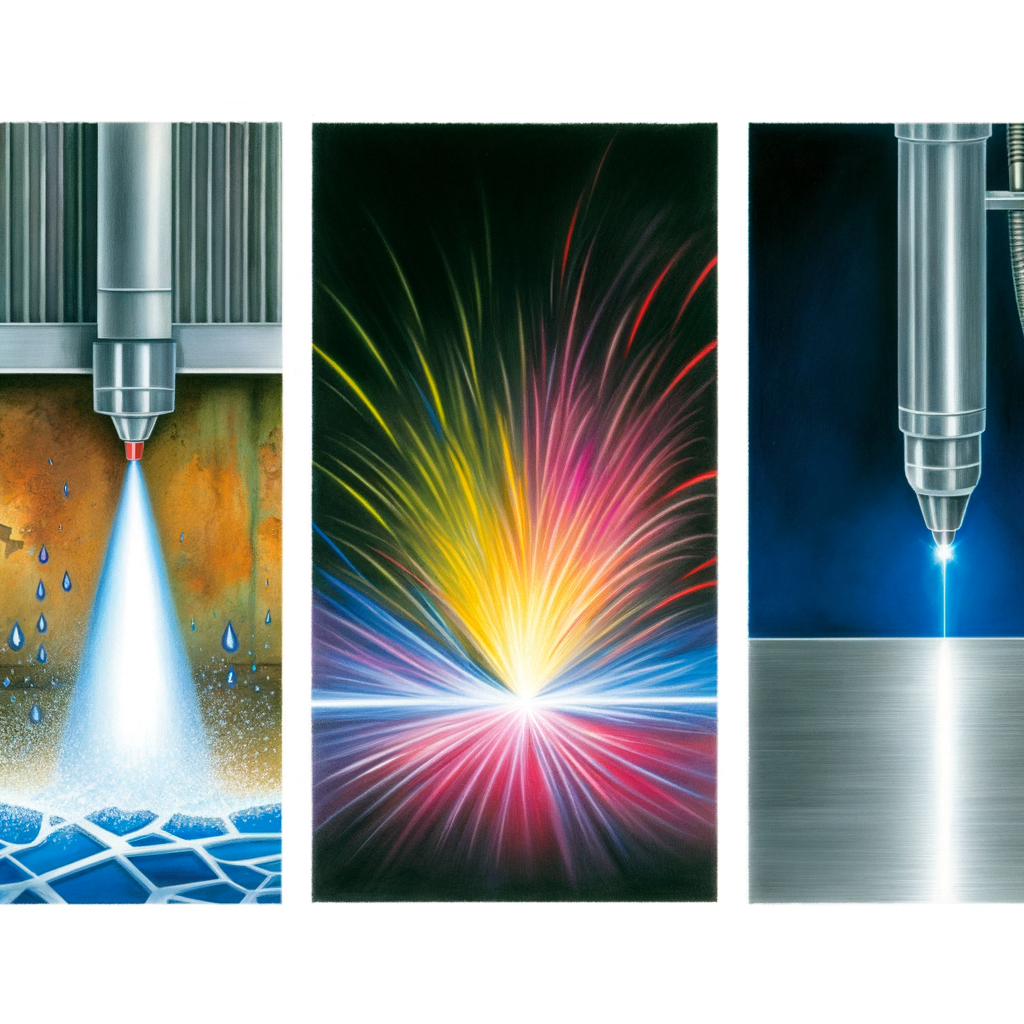

When it comes to cutting through materials for manufacturing, fabrication, or artistic purposes, the modern craftsman has a variety of sophisticated tools at their disposal. Among the most prevalent are waterjet, plasma, and laser cutting systems, each with its unique advantages and limitations. Deciding which technology is best suited for your project requires a careful consideration of the materials involved, the precision required, the desired speed of production, and cost constraints.
Waterjet cutting is a versatile and powerful process that uses a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with an abrasive substance, to slice through materials. One of the primary benefits of waterjet cutting is its ability to cut through virtually any material, including metals, plastics, glass, ceramics, and composites, without introducing heat or significant stresses. This means that there is no heat-affected zone (HAZ), which can alter the properties of the material near the cut. Additionally, waterjet cutting is known for its high precision and excellent edge quality, which often reduces or eliminates the need for secondary finishing processes. However, it is generally slower than plasma or laser cutting and can be more expensive due to the cost of the abrasive materials and the maintenance required for the equipment.
Transitioning to plasma cutting, this method is particularly well-suited for cutting through conductive metals such as steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. Plasma cutting works by sending an electric arc through a gas that is passed through a constricted opening. The gas is heated to an extremely high temperature and ionized so that it becomes plasma, which efficiently cuts through the metal. Plasma cutting is faster than waterjet cutting and is more cost-effective for thicker metal materials. However, it does produce a HAZ, which may not be desirable for certain applications. Additionally, while plasma cutting is precise, it does not match the fine detail achievable with waterjet or laser cutting.
Laser cutting, on the other hand, uses a focused beam of light to melt, burn, or vaporize material. It is renowned for its precision and speed, making it ideal for applications that require intricate detail and high production rates. Laser cutting is highly effective on a range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and fabrics. The precision of laser cutting means that parts can often be produced with little to no finishing required. However, like plasma cutting, laser cutting does create a HAZ, and the range of materials it can cut is not as extensive as that of waterjet cutting. Additionally, the initial investment and operating costs for laser cutting systems can be higher than for plasma cutting.
In determining which cutting technology is best for your needs, consider the material thickness and type. For thick, conductive materials, plasma cutting offers a cost-effective and speedy solution. For projects that demand high precision without thermal distortion, waterjet cutting is unparalleled. If your project involves thinner materials and requires intricate detail, laser cutting is likely the most suitable choice.
Ultimately, the decision between waterjet, plasma, and laser cutting will hinge on a balance between the desired quality of the cut, the speed of production, the material being cut, and the project’s budget. Each method has its place in modern manufacturing and fabrication, and by carefully assessing the specific needs of your project, you can select the technology that will deliver the best results. Whether you prioritize versatility, speed, precision, or cost, there is a cutting solution that will meet the demands of your creative or industrial endeavors.
The Pros and Cons of Waterjet, Plasma, and Laser Cutting Systems
Waterjet vs Plasma vs Laser – Which is Best For Your Needs?
In the realm of industrial cutting, three technologies stand out for their precision and versatility: waterjet, plasma, and laser cutting systems. Each method offers unique advantages and limitations, making the choice between them a matter of matching the technology to the specific needs of the application. Understanding the pros and cons of each system is crucial for manufacturers and fabricators to make informed decisions that optimize productivity, cost-efficiency, and quality.
Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasive particles, to cut through materials. One of its most significant advantages is its versatility. Waterjets can slice through a wide range of materials, including metals, stone, glass, and composites, without introducing heat or thermal distortion. This makes it an excellent choice for materials that are sensitive to high temperatures. Additionally, waterjet cutting is environmentally friendly, as it does not produce hazardous waste and the water used can often be recycled. However, waterjet systems tend to be slower than plasma and laser cutters and can be more expensive to operate due to the high cost of abrasive materials and maintenance.
Transitioning to plasma cutting, this technology utilizes a high-velocity jet of ionized gas heated to an extremely high temperature to melt and expel material from the cut. Plasma cutters are known for their speed, especially when cutting through conductive metals such as steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. They are more cost-effective than waterjet systems for cutting thicker metal sheets and have a relatively low operating cost. Nevertheless, plasma cutting is less precise than waterjet or laser cutting, and the heat-affected zone can lead to material warping or changes in material properties. This makes plasma cutting less suitable for intricate or precision applications.
Laser cutting, on the other hand, harnesses the power of a focused laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize material. It offers unparalleled precision and repeatability, making it ideal for detailed and intricate cuts. Laser cutters can work with a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood, and they operate at high speeds with minimal kerf width. The precision of laser cutting also means that less material is wasted, which can be a significant cost-saving factor. However, the initial investment for laser cutting equipment is typically higher than for plasma or waterjet systems. Moreover, the range of material thickness that laser cutters can handle is more limited, and they may struggle with reflective materials or those that are prone to thermal damage.
In conclusion, the choice between waterjet, plasma, and laser cutting systems depends on a careful consideration of the material to be cut, the desired precision, the thickness of the material, and budget constraints. Waterjet cutting is the go-to for diverse materials and heat-sensitive applications, plasma cutting excels in speed and cost-effectiveness for thicker metals, and laser cutting stands out for its precision and clean cuts in thinner materials. By weighing these pros and cons, manufacturers and fabricators can select the cutting technology that best aligns with their operational needs and ensures the highest quality of the finished product.
Conclusione
The best cutting technology for your needs—waterjet, plasma, or laser—depends on the specific requirements of your application, including material type, thickness, precision, edge quality, and cost-efficiency.
Waterjet cutting is versatile, able to cut a wide range of materials without heat-affected zones (HAZ), making it ideal for materials sensitive to high temperatures. It provides excellent edge quality and does not require secondary finishing. However, it is slower and more expensive than plasma cutting.
Plasma cutting is cost-effective for cutting thicker metal materials quickly. It is less precise than laser and waterjet cutting and may produce a HAZ, which could be a drawback for certain applications.
Laser cutting offers high precision and speed, especially for thin to medium-thick metals. It produces a high-quality edge finish with minimal HAZ but can be less effective for reflective materials and is generally more expensive than plasma cutting.
In conclusion, choose waterjet for versatility and non-thermal cutting, plasma for cost-effective cutting of thicker materials, and laser for high precision and speed on thin to medium-thick materials. Consider the specific needs of your project to determine the best cutting technology.



Lascia un commento